Investment―Stagflation 2.0
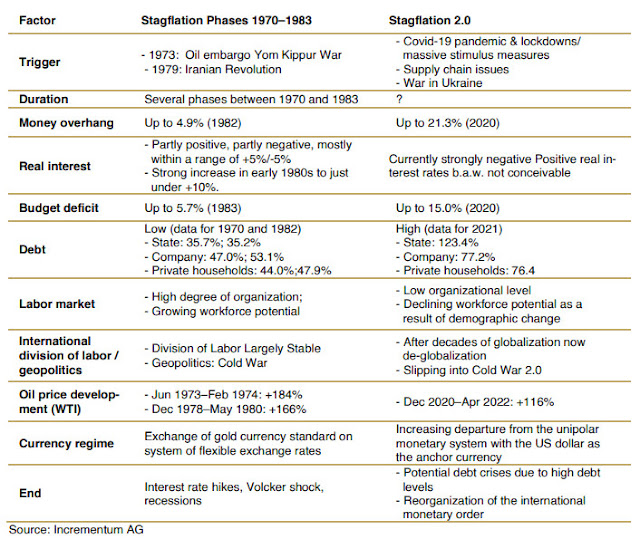
Table 1. Stagflation 1.0 (1970-1983) vs 2.0 Stagflation , or recession-inflation, is an economic phenomenon marked by persistent high inflation, high unemployment, and stagnant demand in a country's economy. [1] During a particularly severe period of economic conditions in the 1970s , rising inflation and slumping employment put a damper on economic growth in the United Kingdom and seven other major market economies, and investors in equity markets suffered greatly as a result. Historically, the last pronounced stagflation phases occurred between 1970 and 1983. These were made possible by a liquidity overhang, which had its origins in an excessively loose monetary policy, and were triggered by oil shocks caused by geopolitical tensions. [2] Stagflation 2.0 In its " In Gold We Trust " report, incrementum (i.e., a fund and asset management firm) believes we're in another period of stagflation and minted the term "stagflation 2.0". We will certainly not hav...

